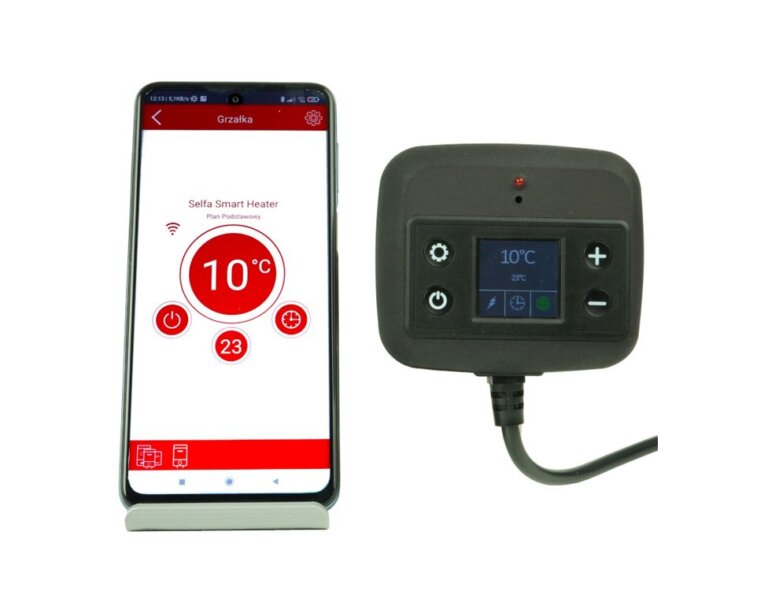
The right selection of heating elements
By selection of heating element very important role play application and conditions of work. Size, power and surface load of heating element depend on different factors. To satisfy your needs fully we need to find out your exact requirements with respect to:
- application
- heated medium
- required temperature
- permissible size
- rated voltage
- rated power
- electric terminals
- control of temperature
Required temperature
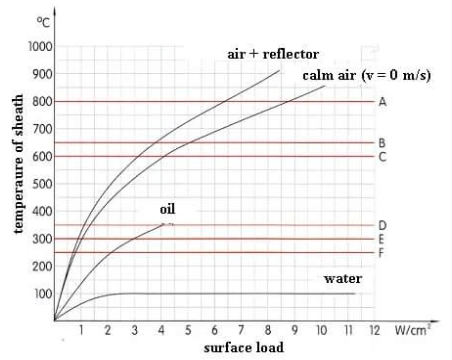
| Material of sheath | Permissible maximum temperature |
| A – steel alloy 20%Cr 30%Ni (e.g. Incoloy 800) | max. 800 °C |
| B – steel alloy 18%Cr, 9%Ni (e.g. AISI-321) | max. 650 °C |
| C – chromium steel | max. 600 °C |
| D – carbon steel | max. 350 °C |
| E – aluminium | max. 300 °C |
| F – copper, brass | max. 250 °C |
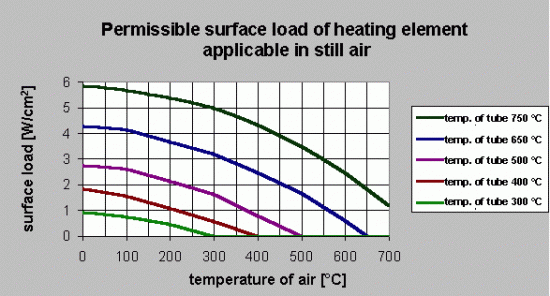
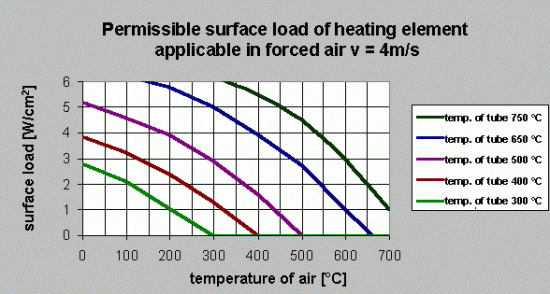
Surface load
Permissible surface loads of heating elements in W/cm2 vary with conditions of work
| Application | Materiał rurki | |||
| cooper | steel | steel alloy (AISI 304) | steel alloy (Incoloy 800) | |
| still water | 10 | – | 10 | – |
| forced water | 14 | – | 14 | – |
| forced water (immediate water heaters) | 25 | – | 25 | – |
| water vapour | 6 | – | 6 | – |
| thin oil | – | 3,5 | 3,5 | – |
| thick oil | – | 1,2 | 1,2 | – |
| special heating oil (heaters)) | – | 12 | 12 | – |
| still air | – | 1,7 | 5 | 6 |
| forced air v=2 m/s | – | 2 | 5,5 | 6,5 |
| forced air v=10 m/s | – | 5 | 10 | 10 |

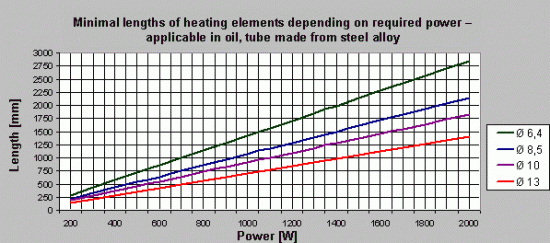
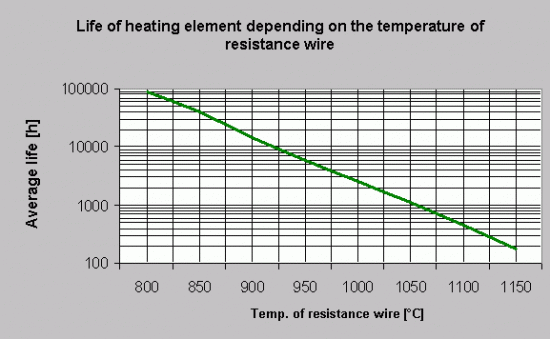
Trwałość
Przeciętny czas pracy elementu grzejnego zależy głównie od temperatury pracy wewnętrznego drutu oporowego, która to z kolei jest funkcją temperatury powierzchniowej płaszcza oraz obciążenia powierzchniowego części grzejnej elementu.